Your Definitive Malignant growth Glossary
Your Definitive Malignant growth Glossary. The news that you are experiencing malignant growth is as of now challenging to settle to. The circumstance might appear to be considerably more troublesome when you don’t grasp the language of your oncologist. A significant chunk of time must pass to handle the new disease languages tossed at you.
New and inadequate information about disease and its connected side effects can wind up frightening you much more. Besides, in the event that you are know all about the words related with this sickness, it becomes simpler for you to cooperate with your PCP to battle the condition. Here, we assist you with doing that.
Adjuvant Treatment:
It alludes to the therapy that you bring with your principal therapy to decrease or prevent the possibilities of malignant growth from returning.
Angiogenesis Inhibitors:
These are extraordinarily planned drugs that stop the development of fresh blood vessels and forestall blood stream to the dangerous growth. This medication may not kill the growth but rather can prevent disease from spreading to other body parts.
Antiemetic:
This is a medication that assists with forestalling spewing and squeamishness, which are the normal results of some malignant growth medicines.
Allogenic undeveloped cell relocate:
A hereditarily matched undifferentiated organism benefactor gives immature microorganisms to the disease patient. Generally such a giver is the patient skin who has a similar tissue type. The contributor s solid immature microorganisms are utilized to supplant the patient’s undesirable undifferentiated cells. High portions of chemotherapy and radiation are utilized simultaneously.
Organic Treatment:
It is an umbrella term for treatment modalities like immunotherapy, quality treatment, and so on. In natural treatment medicines are completed by utilizing items made from living sources, like human or creature cells or a microorganism. While some a portion of these therapies assault specific disease cells, others influence your insusceptible framework (further developing it or making it less dynamic) or decrease malignant growth secondary effects.
Your Definitive Malignant growth Glossary
Biomarker:
Biomarkers or growth markers allude to specific substances in your blood, other body liquids, or tissues that are recognized through a blood test. They are normally made of malignant growth cells. They can assist your primary care physician with recommending the best therapy for you, by uncovering how your body is answering a specific therapy or on the other hand on the off chance that disease has spread or returned.
Biopsy:
Here a little example of your tissue is taken out and shipped off the research facility for testing. Diagnosing cancer is typically utilized. Your PCP could utilize a needle, or a slender, adaptable cylinder intended to do the method. It normally harms very little since the impacted region is desensitized ahead of time.
BI-RADS 4
BI-RADS or Bosom Imaging Report and Information Framework is a symptomatic technique used to portray the discoveries of mammograph results. Mammograph results are ordered as BI-RADS 0-6. These grades demonstrate low to high helplessness to disease. On the off chance that somebody’s cancer is evaluated as BI-RADS 4A, the radiologist proposes a biopsy.
BRCA1 and BRCA2:
These are two qualities, which, when transformed, increment the gamble of bosom, prostate, and ovarian tumors.
Chemotherapy:
A therapy utilizes cytotoxic medications to obliterate malignant growth cells. Chemotherapy is given intravenously (in the vein), orally (by mouth), and by different courses of organization to obliterate or slow the development of malignant growth cells.
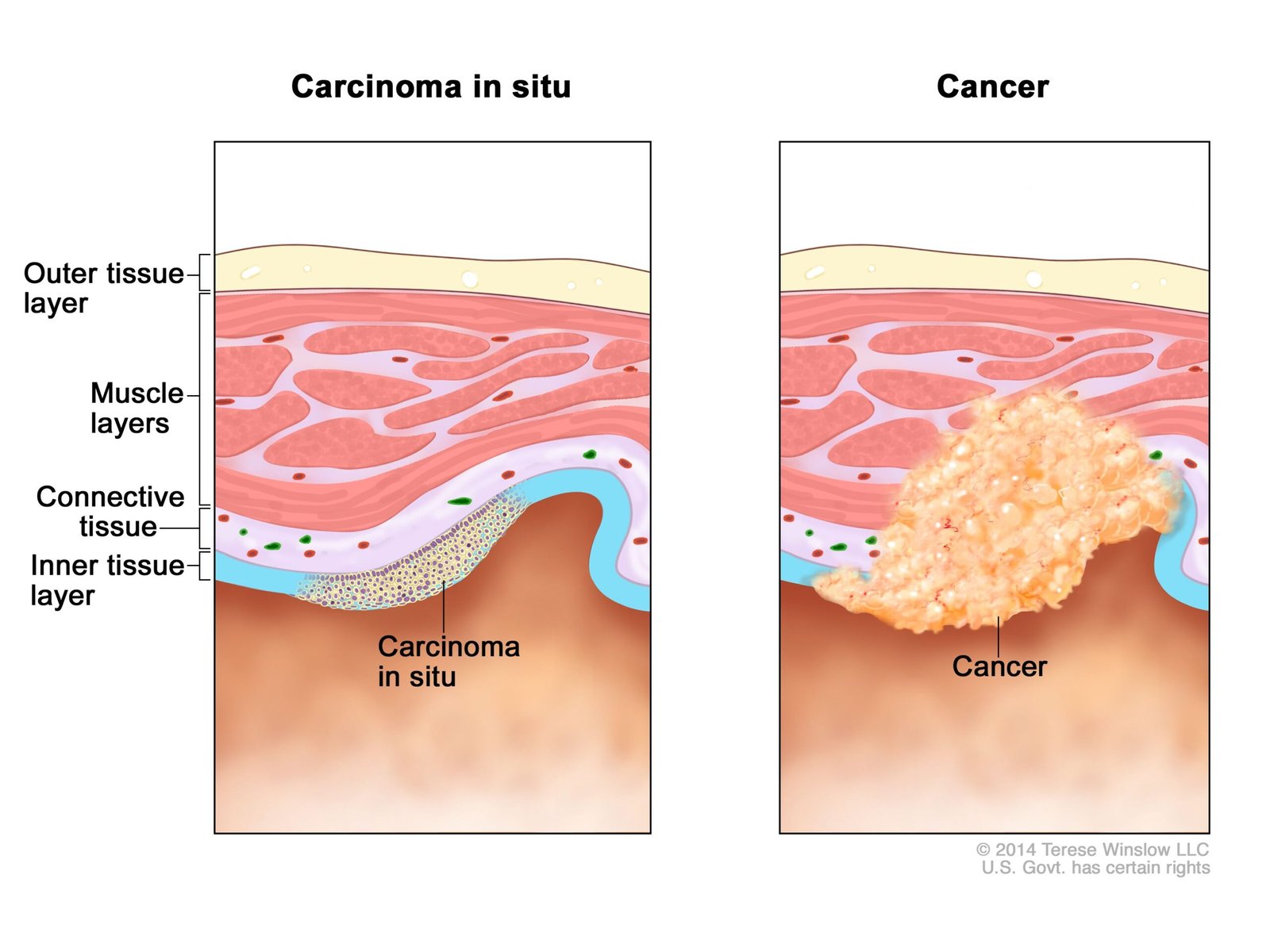
Carcinoma:
It alludes to the kind of malignant growth that begins in skin cells or tissue lining organs like liver or kidneys. This sort of disease incorporates basal and squamous cell carcinoma (skin malignant growths), renal cell carcinoma (kidney malignant growth), and so on.
Constant Myeloid Leukemia (CML):
This disease is described by uncontrolled development of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and their collection in the blood.
Cancer-causing agent:
These are substances that increment the possibilities creating malignant growth, for example, tobacco smoke, bright daylight, asbestos, and so on.
Dysplasia:
These are unusual cells in a tissue that develop before the out and out improvement of disease. Normally, this tissue is taken out as a preventive measure.
Grade:
Grade depicts how the growth looks under a magnifying lens. This gives a thought of how rapidly the cancer might develop, spread and assists the specialist with arranging your therapy. Poor quality means the cells have changes that show they are developing gradually. High-grade growths will quite often spread all the more rapidly.
Chemical treatment:
Chemical or endocrine treatment is utilized to treat tumors that depend on chemicals to develop, like bosom and prostate malignant growth. It uses specialists that block the body s capacity to make chemicals or impede chemical usefulness.
HPV:
HPV or Human papillomavirus is an infection obtained through the skin to skin sexual contact. It can bring about genital moles and diseases of the cervix, vulva, penis, rear-end, mouth, and throat. HPV is the most well-known physically communicated disease.
Immunotherapy:
This type of therapy works on your invulnerable framework to assist with battling disease. Immunotherapy assaults malignant growth straightforwardly or animates your safe framework’s capacity to annihilate it. It incorporates designated spot inhibitors (PD-1 and PDL-1 inhibitors), Vehicle T treatment, and malignant growth immunizations.
Lymph Hubs:
Lymph hubs allude to little bean-formed organs that are portions of your lymphatic framework. Lymph hubs under the arm, known as the axillary hubs, channel liquid from the chest and arm. Some lymph hubs are taken out during bosom a medical procedure to decide the phase of malignant growth.
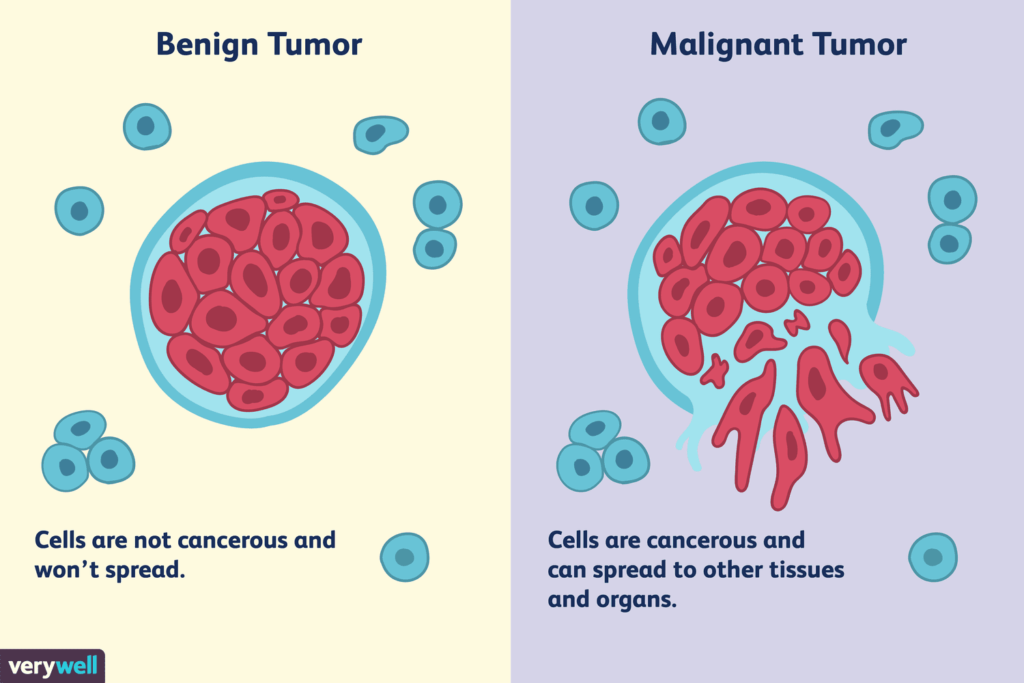
Metastasis:
Metastasis alludes to the spread of disease from where it started to one more piece of the body. Malignant growth cells can split away from the essential growth and travel through the blood or the lymphatic framework to the lymph hubs, cerebrum, lungs, bones, liver, or different organs.
Neoadjuvant treatment:
Neoadjuvant treatment alludes to the therapy given before the primary therapy of malignant growth. It might incorporate chemotherapy, radiation treatment, or chemical treatment utilized before a medical procedure to shrivel a cancer so it is simpler to eliminate.
Stage I malignant growth:
Stage I malignant growth implies that the disease cells are restricted or present in just a single region.
Stage II malignant growth:
Stage II malignant growth implies that the disease is filling in size. Contingent on the sort of disease, stage II malignant growth might spread to the close by lymph hubs. Stage II malignant growths are as yet treatable.
Stage III malignant growth:
Malignant growth in Stage III is bigger in size in contrast with stage II and has spread past the beginning area of the cancer. Much of the time, the disease is found to have attacked close by lymph hubs and muscles. However it is a high level stage, effective treatment choices are accessible.
Stage IV malignant growth:
When malignant growth develops to continue to the fourth stage, it is called terminal disease. The disease has now spread to different pieces of the body. It is the last stage.
Article you might like