Method of conveyance affects child’s wellbeing

Method of conveyance affects child’s wellbeing. A new examination has found that method of conveyance impacts the soundness of babies. The examination introduced at the gathering of ECCMID 2019 proposed that method of conveyance impacts the improvement of the microbial arrangement of the stomach (for example the stomach microbiota) in babies, freely of a mother’s utilization of anti-microbials. This, thus, may influence babies’ respiratory wellbeing during the main year of life.

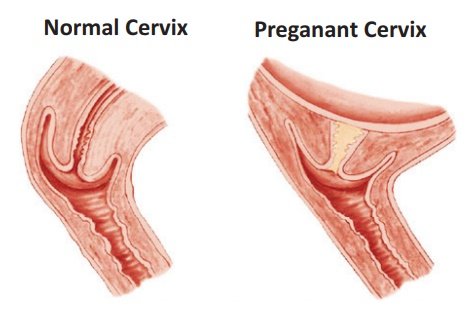
The forthcoming Microbiome Utrecht Infant Study including 120 babies, found that youngsters brought into the world by cesarean segment (C-segment) had a defer in the ordinary improvement of their stomach microbiota, and a higher overflow of possibly unsafe microorganisms, contrasted with babies conveyed vaginally-which could be the system driving the expanded gamble in respiratory diseases.
North of 1000 distinct sorts of microorganisms live in the stomach, where they evoke significant capabilities for wellbeing, for instance assisting with processing food, animating the advancement of the safe framework, and safeguarding against contamination. After birth, newborn children become colonized by a rising variety of stomach microorganisms until a moderately steady state is reached.
The speed and example by which babies gain their stomach microbiome are remembered to significantly affect wellbeing in later life. Disturbance of the ordinary improvement of the stomach microbiome has been connected with a scope of infections including touchy gut sickness, asthma, sensitivities and malignant growth.
Method of conveyance affects child’s wellbeing
Past examination demonstrated that early life microbiota improvement is affected by the method of conveyance, despite the fact that it has been proposed that this relies generally upon maternal anti-infection openness. To evaluate the autonomous impacts of method of conveyance examined the stomach microbiota improvement in 46 C-area and 74 vaginally conveyed babies utilizing feces tests gathered multiple times during their most memorable year of life.
Anti-infection organization to moms going through a C-segment was deferred until subsequent to bracing of the umbilical string. Maternal feces tests were likewise analyzed fourteen days after conveyance.
Examinations showed that stomach microbiota organization varied fundamentally between C-area and vaginally conveyed babies in the principal year, which was most articulated not long after birth. This was joined by quantifiable waste cultivating (move of maternal vaginal organisms) from mother to kid in vaginally conveyed babies, yet not in that frame of mind by C-section.In newborn children brought into the world by C-segment, the stomach microbiota was less steady and the improvement of the wellbeing advancing bacterial species Bifidobacterium spp.
was deferred contrasted with vaginally conveyed children.Additionally, babies brought into the world by C-segment had a lot more significant levels of potential pathogenic stomach microbes, regardless of the length of medical clinic stay after birth, taking care of type, and anti-infection use. Strangely, the scientists likewise found that the stomach microbiota right off the bat in life was related with the absolute number of respiratory contaminations over the main year.
“Our discoveries recommend that method of conveyance influences the creating baby stomach microbiota, free of a mother’s utilization of anti-microbials during birth. Contrasted with vaginally conveyed babies, kids brought into the world by C-area have various directions of bacterial colonization, which could have suggestions for their future respiratory wellbeing”, said Marta Reyman, who is the PhD understudy on this study.”
Further research and bigger investigations will be expected to comprehend the outcomes of these progressions completely. The bits of knowledge acquired could assist with planning techniques to forestall wellbeing related issues following birth by C-segment, Reyman added.
The significant limit of this study is the utilization of 16S rRNA based sequencing, which doesn’t permit explanation of microorganisms on an animal categories level or creates results in view of hereditary substance of microbial networks.
Article you might like